Written by Dr.Albana Greca Sejdini, Md, MMedSc
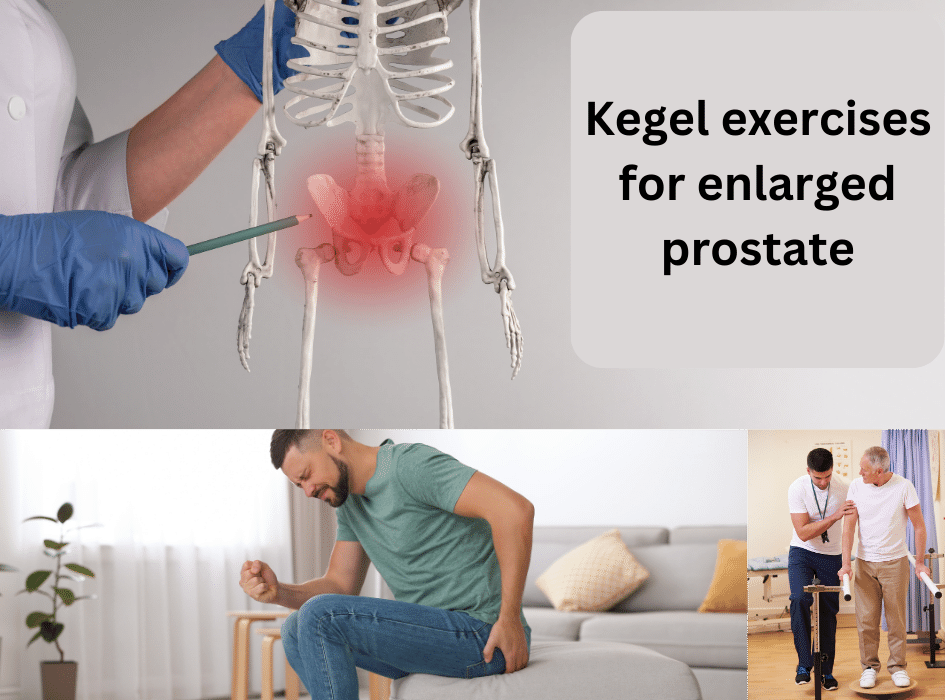
Kegel exercises for enlarged prostate
Kegel exercises, also known as pelvic floor exercises, are often recommended as a non-invasive treatment for men with enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Kegel exercises are simple and can be done discreetly, making them an attractive option for men who want to improve their urinary symptoms without the need for medication or surgery.
What are Kegel exercises?
Kegel exercises involve contracting and relaxing the muscles that form the pelvic floor. These muscles, also known as the pubococcygeus (PC) muscles, support the bladder, prostate, and rectum.
Strengthening these muscles can help improve bladder control and reduce urinary symptoms such as urgency, frequency, and leakage.
How to perform Kegel exercises?
In order to perform Kegel exercises, a man should:
- Identify the muscles: The first step is to identify the pelvic floor muscles. To do this, a man should try to stop the flow of urine while urinating. The muscles used to stop the urine flow are the same muscles that need to be contracted during Kegel exercises.
- Contract the muscles: Once the muscles have been identified, a man should tighten them and hold for 5-10 seconds, then relax for the same amount of time. It is important to focus on contracting only the pelvic floor muscles and not the abdomen, buttocks, or thighs.
- Repeat: A man should aim to do 10-15 repetitions of Kegel exercises, 3-4 times a day.
Benefits of Kegel exercises for enlarged prostate
Kegel exercises have been shown to be effective in improving urinary symptoms in men with enlarged prostate or BPH.
Studies have found that men who perform Kegel exercises regularly have a significant reduction in urinary symptoms and improved quality of life.
Here are some of the benefits of Kegel exercises for enlarged prostate:
- Improved bladder control: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help improve bladder control and reduce urinary leakage.
- Reduced urinary symptoms: Kegel exercises can help reduce urinary symptoms such as urgency, frequency, and nocturia (waking up at night to urinate).
- Improved sexual function: The pelvic floor muscles are also important for sexual function. Strengthening these muscles can improve erectile function and reduce premature ejaculation.
- Non-invasive: Kegel exercises are a non-invasive treatment option for enlarged prostate. They do not require medication or surgery, and can be done discreetly.
Tips for performing Kegel exercises
Here are some tips to help you get the most out of your Kegel exercises:
- Be consistent: Like any exercise program, consistency is key. Aim to do Kegel exercises at least 3-4 times a day, every day.
- Relax: It is important to relax the pelvic floor muscles between contractions. This will help prevent muscle fatigue and improve the effectiveness of the exercises.
- Use visual cues: Some men find it helpful to use visual cues to help them contract the pelvic floor muscles. For example, imagine you are trying to lift a marble with your penis, or imagine you are trying to stop passing gas.
- Don't hold your breath: It is important to breathe normally during Kegel exercises. Holding your breath can increase abdominal pressure and make it more difficult to contract the pelvic floor muscles.
- Be patient: It may take several weeks or even months to see significant improvement in urinary symptoms. Be patient and continue with your exercises.
In conclusion, Kegel exercises are a safe and effective non-invasive treatment option for men with enlarged prostate or BPH. They can help improve bladder control, reduce urinary symptoms, and improve sexual function.
If you are experiencing urinary symptoms, talk to your healthcare provider about incorporating Kegel exercises into your treatment plan. Your healthcare provider can also provide guidance on how to perform Kegel exercises correctly and monitor your progress.
It is important to note that Kegel exercises may not be effective for all men with enlarged prostate or BPH. In some cases, medication or surgery may be necessary to manage urinary symptoms. Your healthcare provider can help determine the best treatment option for your individual case.
How lifestyle changes can help with Kegel Exercises?
In addition to Kegel exercises, there are other lifestyle changes that may help improve urinary symptoms in men with enlarged prostate or BPH. These include:
- Limiting fluid intake before bedtime: Avoiding fluids 2-3 hours before bedtime can help reduce nighttime urination.
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can irritate the bladder and worsen urinary symptoms.
- Staying physically active: Regular exercise can help improve urinary symptoms and overall health.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can put extra pressure on the bladder and worsen urinary symptoms.
- Managing stress: Stress can worsen urinary symptoms. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress and improve urinary symptoms.
In summary, Kegel exercises are a simple and effective non-invasive treatment option for men with enlarged prostate or BPH. They can help improve bladder control, reduce urinary symptoms, and improve sexual function.
|
Written by Dr.Albana Greca Sejdini, Md, MMedSc |
Last reviewed 03/07/2023 |
References
References
- Dorey, G., Speakman, M. J., & Feneley, R. C. (1999). Pelvic floor exercises for treating post micturition dribble in men with erectile dysfunction. The Journal of urology, 162(2), 433-436.
- FitzGerald, M. P., & Kotarinos, R. (2003). Rehabilitation of the short pelvic floor: a review of the evidence. International urogynecology journal, 14(4), 261-268.
- Glazener, C. M. A., Herbison, G. P., MacArthur, C., & Grant, A. (2006). Electrical stimulation with non-implanted electrodes for urinary incontinence in men. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (2).
- Lai, H. H., Hsu, J. W., & Nguyen, L. (2017). Nonpharmacologic Management of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports, 12(1), 13-22.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2018). Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia). Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/prostate-problems/prostate-enlargement-benign-prostatic-hyperplasia
- University of California San Francisco Health. (n.d.). Kegel Exercises for Men. Retrieved from https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/kegel-exercises-for-men
- Woo, H. H., Wynberg, J. B., & Zaslau, S. (2014). Evidence-based analysis of the impact of pelvic floor muscle exercises on symptoms of male urinary incontinence. Current urology reports, 15(9), 1-9.
- Home
- Natural Remedies
- Kegel Exercises for Enlarged Prostate